How GenAI is transforming data interpretation in 2026
Generative AI in Analytics
Discover how generative AI is transforming business analytics by 2026. Learn why Gartner predicts 60% of dashboards will be replaced by AI-generated insights and narratives.

How GenAI is transforming data interpretation in 2026
Generative AI in Analytics
Discover how generative AI is transforming business analytics by 2026. Learn why Gartner predicts 60% of dashboards will be replaced by AI-generated insights and narratives.
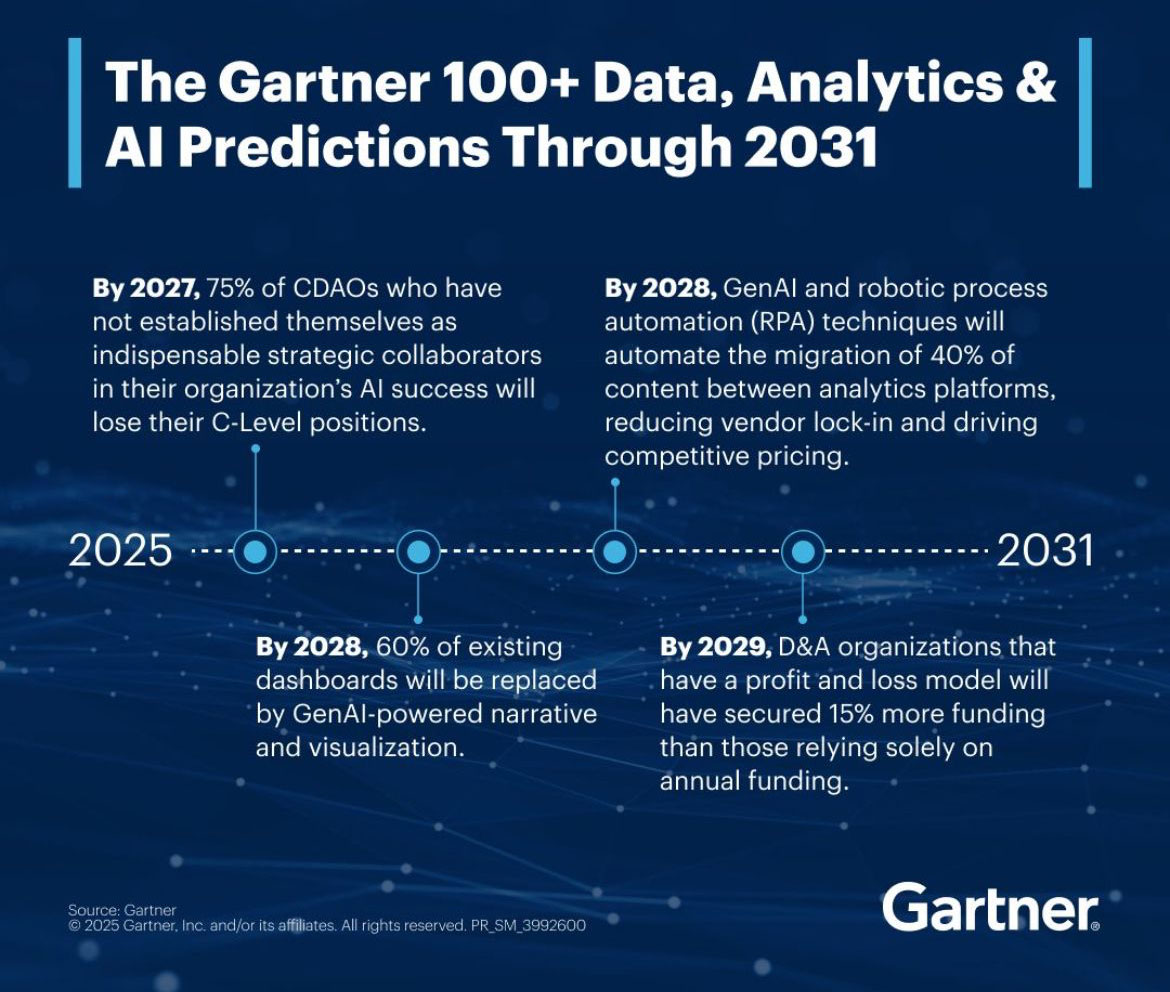
Business analytics is undergoing a transformation. Gartner predicts that by 2028, 60 percent of current dashboards will be replaced by narratives and visualizations produced by generative AI. This is not just a technological upgrade, but a fundamental change in how organizations interpret data and make decisions.
What does generative AI in analytics mean?
Generative AI in analytics brings large language models (LLMs) into the entire data pipeline and transforms data utilization from reporting to decision support. Instead of business users spending time browsing reports or building technical queries, they can ask the system direct questions and receive immediately understandable answers. This accelerates decision-making, improves information accessibility, and helps organizations respond to changes more agilely.
Traditional analytics focuses on describing the past or predicting the future, but generative AI goes much further: it can create new content based on data. In practice, this means that when a user asks a question in natural language (for example, "Why did sales drop in May?"), GenAI can automatically formulate the necessary query, retrieve the right data, perform data processing, and produce a clear text summary, recommendation, or visualization of the results.
This approach democratizes data-driven management in two ways. First, it opens deep data analysis to users without technical backgrounds or coding skills. Second, it lightens the workload of data professionals by automating time-consuming routines such as data cleaning, query writing, and drafting recurring reports. The result is faster decision-making, wider use of analytics, and better visibility across the organization into business cause-and-effect relationships.
Limitations of traditional dashboards
Static information in a dynamic world
Traditional dashboards are essentially snapshots of the past, like photographs of business history. They show what has happened, but don't explain why it happened or what should be done next. For example, a sales director might notice on a dashboard that sales have decreased 15 percent in a certain region. The number alone doesn't reveal whether the decline is due to a competitor, delivery problems, price changes, customer behavior, or some other underlying factor. The dashboard answers "what happened", but leaves the user to ponder "why" and "what next".
Data interpretation
Traditional analytics often requires the ability to read complex tables, build queries, and interpret data in a broader context. This creates a situation in organizations where data is abundant, but only a few know how to use it effectively. A large portion of staff then make decisions without easy access to understandable information. According to Gartner, as many as 80% of business decisions are still made based on intuition or insufficient data. Not because data doesn't exist, but because its interpretation is perceived as difficult.
Time lag from insight to action
In traditional processes, the emergence of insight and decision-making are often too far apart. If an analyst must first create a report, check data quality, produce visualizations, and present findings to management, days or even weeks may pass before necessary actions can be initiated. In a fast-paced business environment, this delay can lead to lost sales opportunities, increasing costs, or strategic misjudgments. When markets change rapidly, mere reporting is no longer enough; fast analyses and recommendations are needed to help make decisions at the right moment.
How generative AI solves these problems
1. Contextual, plain-language explanations
GenAI analytics automatically produces narratives that explain the meaning of data.
Traditional dashboard: "Regional sales: -15%"
GenAI narrative: "Region B sales have decreased 15% over the last month. The decline is primarily due to a competitor's new product launch and the expiration of contract periods with three key customers. Recommendation: Activate the customer retention program and offer a 10% discount on renewal contracts over the next two weeks."
2. Predictive and proactive analytics
Generative AI doesn't just report the past, but anticipates future trends and suggests actions. It identifies anomalies in real-time and provides automatic alerts.
3. Democratized data analytics
Natural language queries make analytics accessible to everyone. A sales director can ask: "Why were Q3 targets not met in Northern Europe?" and immediately receive a comprehensive analysis, without SQL queries or a data analyst's help.
4. Dynamic, customized visualizations
GenAI automatically creates visualizations that best meet each user's needs and questions. The same data can be presented to a CFO as a financial trend analysis and to a product manager as a user experience map.
Examples of use cases across industries
Retail: Inventory optimization
Generative AI can be leveraged in inventory management by combining sales history, external forecasts (such as weather and events), and current trends. The system produces plain-language, predictive recommendations for business users to improve product availability.
Benefits:
- Better demand forecasting
- Faster response to changes
- Less waste and more efficient capital use
Finance and insurance: Risk management
Generative AI supports risk management by forming comprehensive risk profiles from multiple data sources. Instead of decisions being based on individual metrics, the system explains risk changes and their underlying factors in an understandable way.
Benefits:
- Better risk anticipation
- More transparent and justified decisions
- Better balance between risk and return
Healthcare and public services: Resource optimization
Generative AI can be used for demand forecasting and resource allocation in environments where load varies rapidly. The system predicts future demand and suggests concrete actions for personnel and capacity management.
Benefits:
- Shorter waiting and throughput times
- Better service quality and customer experience
- More efficient resource use and cost management
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance
In industrial environments, generative AI can be used to analyze equipment and sensor data. This allows identification of anomalies and anticipation of failures. The system not only alerts to risks but recommends optimal maintenance actions from a business perspective.
Benefits:
- Fewer unplanned production interruptions
- Lower maintenance and downtime costs
- Better overall production efficiency
Technical implementation: How GenAI analytics works
Integrating generative AI into analytics requires the cooperation of multiple components. It's not a simple add-on to existing systems, but a comprehensive architectural approach that combines traditional analytics tools, modern cloud services, and advanced AI solutions. Successful implementation requires careful planning from both technical and organizational perspectives.
The technical architecture of GenAI analytics is typically built in layers. At the bottom is the data layer, where the company's various data sources and data warehouses are located. On top of this operates the integration layer, which enables seamless data transfer between different systems. The analytics layer contains both traditional BI tools and modern ML models, while at the top operates the GenAI layer, which provides a natural language interface and automatic generation of analysis. The interaction between these layers is critical for system efficiency.
Implementation success also depends on how well the organization manages to balance innovation and practicality. An overly ambitious project can collapse under its own complexity, while an overly cautious approach may not produce sufficient business value to justify the investments.
1. Data infrastructure
Effective GenAI analytics requires a unified data architecture where data from different sources is available in real-time. This can mean a data lakehouse architecture or a modern data fabric solution.
2. Language models and context management
At the core of the system is a large language model that is either tailored to the company's industry or specialized with the organization's own data. The model must understand the business context, terminology, and KPIs.
3. Analytics engine
GenAI is connected to an analytics engine that performs the actual data processing, statistical analysis, and machine learning models. The language model acts as the interface and interpreter.
4. Security and governance
It is critical to ensure that the GenAI system complies with data access rights, protects sensitive information, produces traceable, auditable results, and adheres to applicable regulations.
Implementation challenges and solutions
Challenge 1: Data quality and consistency
GenAI is only as good as the data it operates on. Broken, inconsistent, or erroneous data leads to misleading insights.
Solution: Start with a data governance program that standardizes data collection, storage, and quality control. Implement a data catalog and metadata management.
Challenge 2: User trust and adoption
People are skeptical of "black box" recommendations, especially in critical business decisions.
Solution: Choose a GenAI solution that offers "explainable AI" features. The system must be able to justify its conclusions and show what data they are based on. Start with a pilot on low-risk use cases and build trust gradually.
Challenge 3: Integration with legacy systems
Many organizations use decades-old ERP and CRM systems, whose integration with a modern GenAI platform is complex.
Solution: Leverage API-based integrations and middleware solutions. Consider a phased approach where GenAI is first added to the newest systems and later expanded to other systems.
Challenge 4: Costs and ROI
GenAI technology can be expensive, and demonstrating return on investment can be challenging.
Solution: Start with a clearly defined use case that has measurable KPIs. Calculate ROI both as direct savings (e.g., reduced analyst hours) and indirect benefits (faster decision-making, better customer experience).
The future of GenAI analytics: What's coming?
Multimodal analytics
Next-generation GenAI systems will simultaneously analyze structured data, text, images, and videos. For example, in retail, the system could analyze customer behavior in stores from video footage in addition to sales figures and produce comprehensive recommendations.
Autonomous decisions
Generative AI is gradually moving from recommending to autonomous decision-making in low-risk situations. For example, in inventory management, the system won't just suggest but will automatically place orders with suppliers within defined parameters.
Collaborative analytics
Future GenAI tools will work in collaboration with multiple decision-makers, facilitating group decisions and combining different perspectives. The system could, for example, coordinate a strategy meeting where it provides data-driven perspectives to each participant's questions in real-time.
Summary: Generative AI is transforming the future of analytics
Gartner's prediction of dashboards being replaced by GenAI narratives by 2028 reflects a significant change in how organizations leverage data. Early adopters can achieve concrete advantages in multiple areas.
GenAI analytics enables faster decision-making by transforming data into insights in minutes instead of the traditional hours or days. It democratizes analytics by making data-driven work possible even for those without technical backgrounds. The predictive approach helps identify trends before they become problems, and the system's scalability enables analysis of broader datasets than traditional methods.
Organizations should evaluate when and how generative AI fits into their analytics strategy. The technology is evolving rapidly, and early experimentation provides an opportunity to learn and build expertise gradually.
Empirica Finland specializes in AI solutions for B2B organizations and has helped companies across industries leverage autonomous agents to enhance their operations.
Read next
Start your journey towards GenAI analytics today.
Want to discuss how generative AI could transform your company's analytics?
Contact us